06. What is Cloud Computing & Why Would We Use It?
Cloud Computing
In this section, we will focus on answering two questions:
- What is cloud computing?
- Why would a business decide to use cloud computing?
This section will be a high-level look. However, you can dive more into the details by looking at the optional pages added at the end of this section.
What is cloud computing?
You can think of cloud computing as transforming an IT product into an IT service .
Consider the following example:
Have you ever had to backup and store important files on your computer? Maybe these files are family photos from your last vacation. You might store these photos on a *flash drive*. These days you have an *alternative option* to store these photos in the ***cloud*** using a *cloud storage provider*, like: [Google Drive](https://www.google.com/drive/), [Apple’s iCloud](https://www.apple.com/icloud/), or [Microsoft’s OneDrive](https://onedrive.live.com/about/en-us/).
Cloud computing can simply be thought of as transforming an Information Technology (IT) product into a service . With our vacation photos example, we transformed storing photos on an IT product , the flash drive ; into storing them using a service , like Google Drive .
Using a cloud storage service provides the benefits of making it easier to access and share your vacation photos, because you no longer need the flash drive. You’ll only need a device with an internet connection to access your photos and to grant permission to others to access your photos.
Generally, think of cloud computing as using an internet connected device to log into a cloud computing service , like Google Drive , to access an IT resource , your vacation photos . These IT resources , your vacation photos , are stored in the cloud provider’s data center . Besides cloud storage, other cloud services include: cloud applications, databases, virtual machines, and other services like SageMaker.
Why would a business decide to use cloud computing?
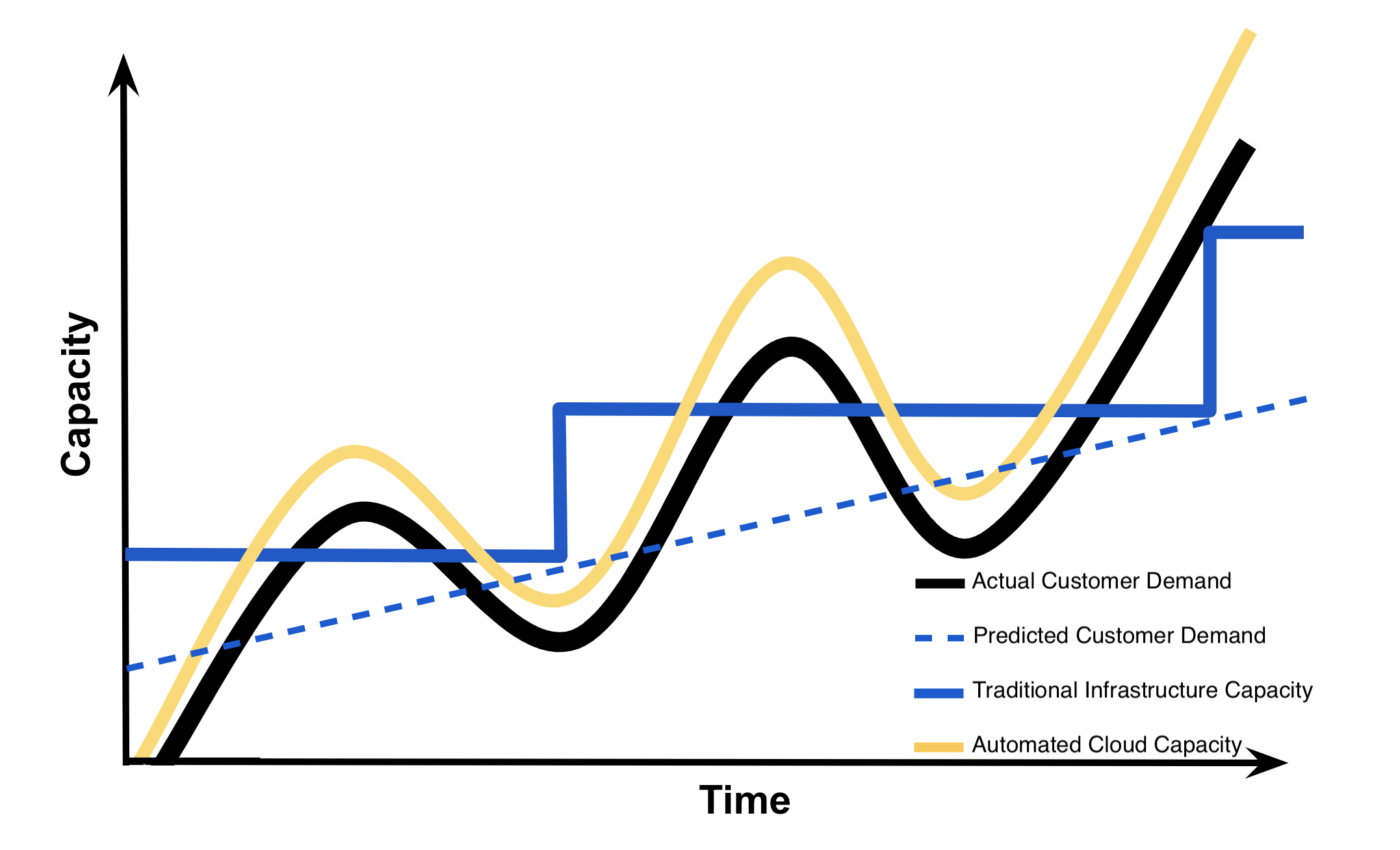
Most of the factors related to choosing cloud computing services , instead of developing on-premise IT resources are related to time and cost . The capacity utilization graph below shows how cloud computing compares to traditional infrastructure (on-premise IT resources) in meeting customer demand .
Capacity in the graph below can be thought of as the IT resources like: compute capacity, storage, and networking, that's needed to meet customer demand for a business' products and the costs associated with those IT resources . In our vacation photos example, customer demand is for storing and sharing customer photos. The IT resources are the required software and hardware that enables photo storage and sharing in the cloud or on-premise (traditional infrastructure).
Looking at the graph, notice that traditional infrastructure doesn't scale when there are spikes in demand, and also leaves excess when preparing for future demand. This ability to easily meet unstable, fluctuating customer demand illustrates many of the benefits of cloud computing .
Summary of Benefits of Risks Associated with Cloud Computing
The capacity utilization graph above was initially used by cloud providers like Amazon to illustrate the benefits of cloud computing. Summarized below are the benefits of cloud computing that are often what drives businesses to include cloud services in their IT infrastructure [ 1 ]. These same benefits are echoed in those provided by cloud providers Amazon ( benefits ), Google ( benefits ), and Microsoft ( benefits ).
Benefits
-
Reduced Investments and Proportional Costs (providing cost reduction)
-
Increased Scalability (providing simplified capacity planning)
-
Increased Availability and Reliability (providing organizational agility)
Below we have also summarized he risks associated with cloud computing [ 1 ]. Cloud providers don't typically highlight the risks assumed when using their cloud services like they do with the benefits , but cloud providers like: Amazon ( security ), Google ( security ), and Microsoft ( security ) often provide details on security of their cloud services. It's up to the cloud user to understand the compliance and legal issues associated with housing data within a cloud provider's data center instead of on-premise. The service level agreements (SLA) provided for a cloud service often highlight security responsibilities of the cloud provider and those assumed by the cloud user.
Risks
-
(Potential) Increase in Security Vulnerabilities
-
Reduced Operational Governance Control (over cloud resources)
-
Limited Portability Between Cloud Providers
- Multi-regional Compliance and Legal Issues
References
**1.** Erl, T., Mahmood, Z., & Puttini R,. (2013). *Cloud Computing: Concepts, Technology, & Architecture.* Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Chapter 3: Understanding Cloud Computing provides an outline of the business drivers, benefits and risks of cloud computing.
Additional Resources
For the purpose of deploying machine learning models, it's important to understand the
basics
of cloud computing. The essentials are provided above, but if you want to learn more about the overall role of cloud computing in developing software, check out the
[Optional] Cloud Computing Defined
and
[Optional] Cloud Computing Explained
sections at the end of this lesson along with the additional resources provided below.
-
National Institute of Standards and Technology formal definition of Cloud Computing .
-
Kavis, M. (2014). Architecting the Cloud: Design Decisions for Cloud Computing Service Models. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Chapter 3 provides the worst practices of cloud computing which highlights both risks and benefits of cloud computing. Chapter 9 provides the security responsibilities by service model.
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS) discusses their definition of Cloud Computing .
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) discusses their definition of Cloud Computing .
-
Microsoft Azure (Azure) discusses their definition of Cloud Computing .